What is a Chemical Peel?
Chemical peels encourage exfoliation by sloughing off dead skin cells, forcing your body to quickly replenish them with new cells. When peels are performed regularly, the skin gets used to this process and begins to rejuvenate itself like younger skin. To be sure that the body doesn’t react to this deep exfoliation as it would to trauma, which can lead to pigment changes, exfoliation must be introduced and gradually giving the skin time to adjust. The results of the procedure depend on the chemical used and its concentration, skin preparation, method of application, contact time, and skin condition. The depth of the peel determines the magnitude of the results, but also the patient’s inconvenience during and after the procedure, the healing time and the rate of potential side effects. Pre-treatment products precondition the skin, accelerate results and minimize complications. Post-treatment products minimize complications, heal and soothe the skin and then maintain the results. Professional treatments enhance the results of your home care products.
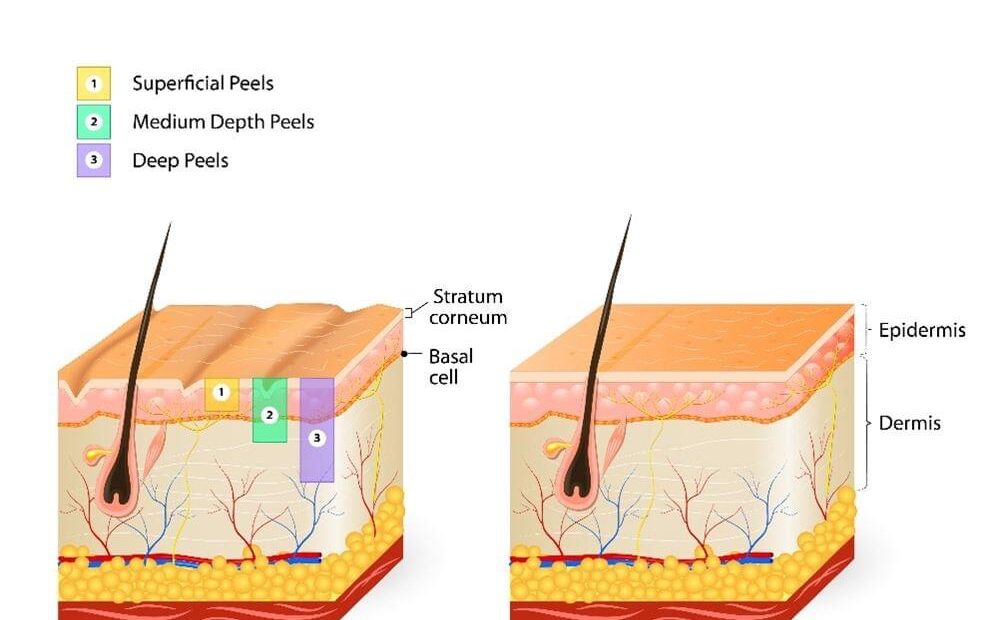
How Are Chemical Peels Classified?
Chemical peels are classified as light (superficial), medium, or deep, depending on the depth of penetration of the ingredients used. Light peels exfoliate to various levels of the epidermis. Medium depth peels treat through the papillary dermis and deep peels to the mid-reticular dermis. Deeper peels require more downtime and increase the chance of side effects, which include photosensitivity, pigment changes and scarring. Deep peels should only be done by an experienced physician such as a dermatologist.
How Do Chemical Peels Work?
Superficial chemical peels decrease the pH at the surface of the skin and change the pH gradient of the stratum corneum. This loosens the connections between dead skin cells including exfoliation and stimulating new cell growth. Medium and deep chemical peels cause protein coagulation and cell necrosis (cell death) in the epidermis and dermis. This includes inflammation and the wound-healing cascade. Both types of peels thicken the epidermis, increase dermal volume and stimulate collagen. The result is smoother and more radiant complexion.
What Are Common Peeling Agents?
Some common peeling ingredients include alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), and retinol. Alpha hydroxy acids include glycolic acid, lactic acid, citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid and mandelic acid. Salicylic acid is a beta hydroxy acid. The strength of the chemical peel is determined by the type of ingredients used, and their concentration and the pH of the formulation. Not all peels are created equally, and one peel type doesn’t suit all. Certain ingredients may be more effective for treating acne, while others may be more successful in treating hyperpigmentation or the signs aging.
Treatment Expectations
The results of the procedure depend on the chemical used and its concentration, skin preparation, method of application, contact time, and skin condition. The depth of the peel determines the magnitude of the results, but also the patient’s inconvenience during and after the procedure, the healing time and the rate of potential side effects. Beautiful, healthy skin doesn’t happen overnight, and treatments take time to show results. A single chemical peel can provide the immediate effects of bright and radiant skin; however, more significant results in treating textural issues, fine lines and inflamed acne could take longer. Multiple treatments might be necessary to obtain optimal results at approximately 4 week intervals. Use home care products consistently and as directed to achieve optimal results. You need to take time for your daily skincare regimen, morning and evening.