Skin Health and the Sun
There are 3 types of ultraviolet radiation: (100nm-400nm)
UVC (100nm-290nm)
· Rays that do not reach the earth’s surface as they blocked by the ozone layer
UVC (290nm-320nm)
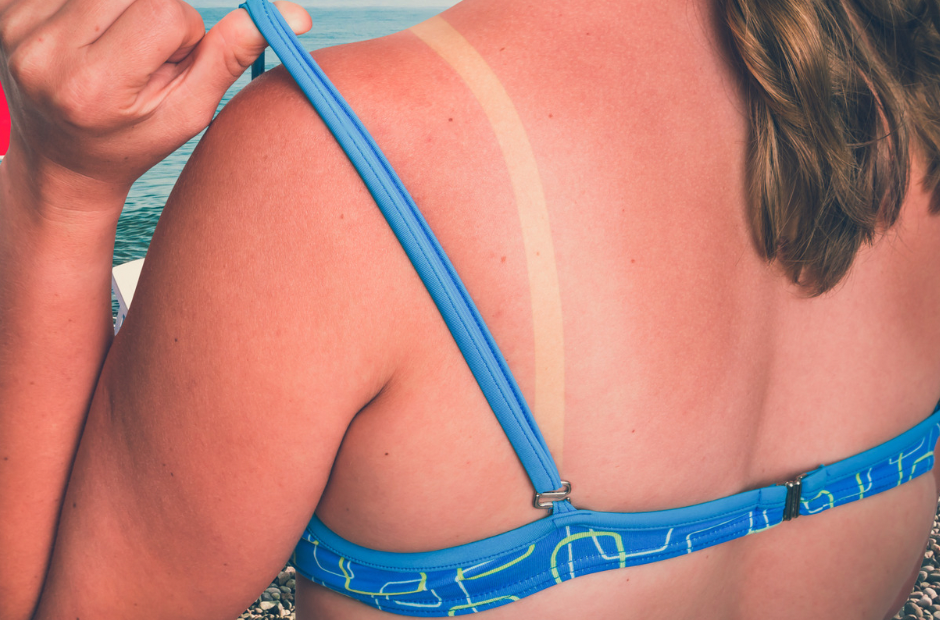
· Rays that cause burning and DNA mutations which lead to skin cancer.
· They are the main cause of sunburn because they damage the skin’s superficial epidermal layers · Play a large role in the development of skin cancer
· Accounts for 5% of the sun’s rays. · More UVB rays have been penetrating the atmosphere because of the thinning ozone layer and increasing the risk of UVB-related sun damage
UVC (320nm-400nm)
· Rays are responsible for photoaging, tanning and DNA mutations which lead to skin cancer
· Deeper penetration into the dermis, producing free radicals that lead to wrinkles, loss of skin elasticity, DNA mutations/skin cancer, and dyspigmentation (abnormality in the formation or distribution of pigmentation in the skin; could appear as hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation). · Are able to pass through glass and clouds
· Accounts for 95% of UV rays that reach the earth · UVA radiation is almost 20 times more abundant compared with UVB
· Have the ability to damage skin cells in the basal layer of the epidermis where most skin cancers arise · Can penetrate deeper (into the dermis) generating free radicals that damage collagen, elastin and blood vessels and deplete protective antioxidants