Free Radicals and Antioxidants
What are free radicals?
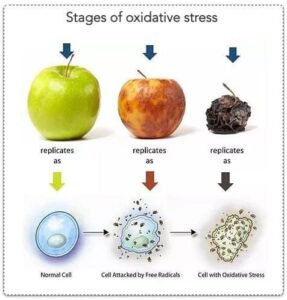
If you’ve ever seen a sliced apple turn brown, you’ve witnessed the process of oxidation, which is caused by free radicals.
Free radicals are highly reactive and unstable molecules that are produced in the body naturally as a byproduct of oxidation/metabolism or by exposure to toxins in the air or environment, like UV rays.
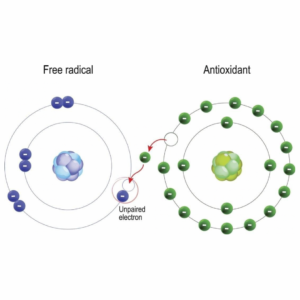
Structurally, they are atoms that contain an unpaired electron, making them unstable; electrons like to be in pairs. A consequence to this is they are in constant search to pair with another electron in order to stabilize.
Why are free radicals bad?
In their search to bond with another electron, they take away or steal an electron from a molecule. This molecule is then missing an electron and becomes a free radical. Free radicals can damage not only DNA molecules, but proteins, lipids, cells, etc, and can potentially cause disease. This creates a domino effect and is termed “oxidative stress”. The body is under constant attack unless antioxidants are used to defend and control oxidative stress.
Where do free radicals come from?
Free radicals come from a variety of different ways.
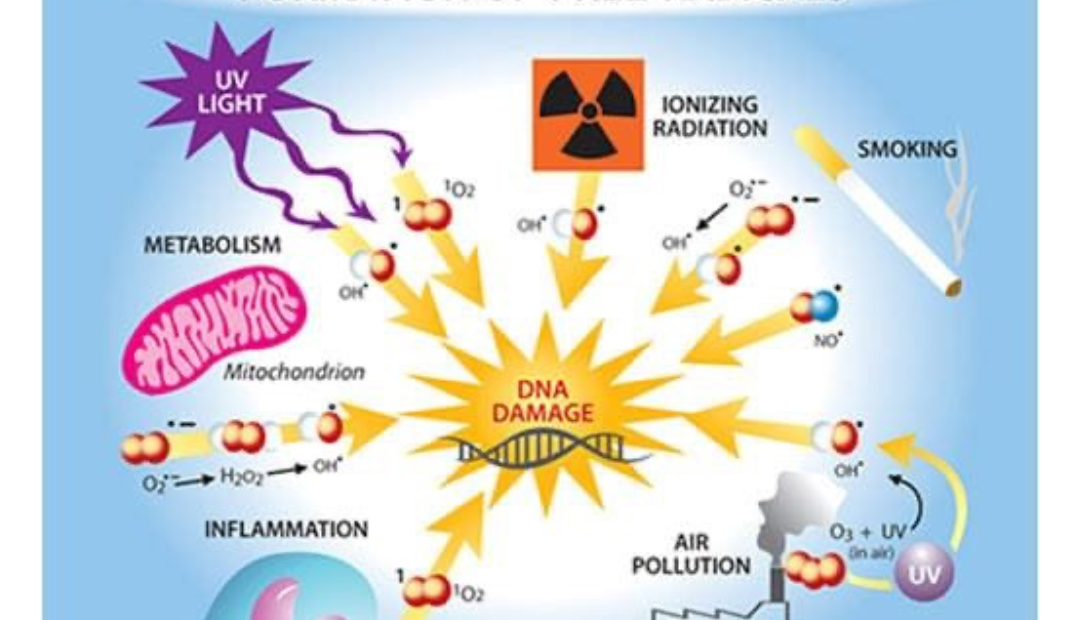
Our body naturally produces free radicals in the process of breaking down nutrients to create energy allowing our bodies to function. This is a normal metabolic process which unfortunately is one reason the risk of cancer increases with age.
Another way in which free radicals are generated is by exposure to cancer causing substances, such as environmental carcinogens, some of which are:
-ultraviolet radiation
-ionizing radiation -environmental pollution
-severe physical and psychological stress -poor nutrition/diet
-alcohol consumption -smoking
So how does this relate to aging?
UV exposure contributes to the majority of free radical production, up to 80%, and is also the most important environmental factor in the development of skin cancer and premature skin aging. Over production of free radicals play a role in extrinsic aging, hyperpigmentation, triggering inflammatory conditions like eczema, rosacea, acne, as well as skin cancers.
Where do antioxidants come in?
There is a delicate balance between free radicals and antioxidants that are natural made in the skin. However, when that balance is disrupted – too many free radicals, fewer available antioxidants (a natural part of aging) – oxidative stress develops.
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants help protect the skin and have anti-inflammatory properties – inflammation impedes the skin’s renewal process. They control and prevent the production of free radicals. They essentially donate electrons to neutralize free radicals or stop them from forming in the first place. Therefore, reducing the damaging events on DNA molecules and cells or in other words oxidative stress. In essence they allow the skin to repair itself and correct visible damage. Avoiding excessive sun exposure and using sun protection also help limit free radicals.
The primary treatment of extrinsic aging and preventing oxidative stress is photoprotection – wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen daily. Just important is the secondary treatment – applying antioxidants daily. Examples of common antioxidants are vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B, and resveratrol. Skincare products with vitamin C and E are recommended for morning use, while vitamin A (retinol) products are recommended for night time use – other forms of vitamin A do not need to be used only at night.