Elastin
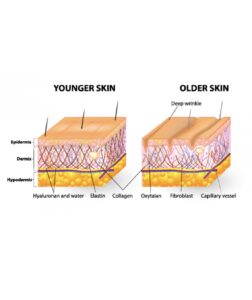
You’ve probably come across the terms collagen and elastin in your research to improving appearance of skin. However, there are similarities and differences between elastin vs collagen, though. Collagen and elastin are the main fibres that form the extracellular matrix. Both are formed by fibroblasts. Additionally, while both are proteins that work together in your connective tissue, collagen is responsible for skin strength and resilience and elastin provides flexibility to the skin and enabling it to return to its original shape or form. Collagen and elastin reside in your skin’s middle layer, called the dermis. This is the thickest of the three layers, accounting for about 90% of your skin’s thickness. There’s a lot going on in this layer, as it’s home to hair, oil, sweat glands, nerves, and blood vessels. Collagen fibers make up 90% of the skin, and elastin makes up 10%.
Production and density of both decreases as a function of age, and results in sagging and wrinkling.
What is Elastin?
Elastin is a naturally occurring, stable protein in the extracellular matrix (ECM) that provides resilience and elasticity to vital organs in the human body. As the main component of elastic fibers, it stores energy. This elastin protein also enables connective tissues to recoil. As a result, elastin is much more flexible than collagen. Elastin is actually 1,000 times more stretchy than collagen. Certain vital tissues in the body contain elastin, including blood vessels, the lungs, and skin. Without your elastin, your skin and other tissues would sag. You can’t get elastin directly from your diet because it occurs naturally through elastin fibrillogenesis.
Over 75% of the makeup of this protein includes just four amino acids:
Proline
Glycine
Valine
Alanine
What Does Elastin Do?
Elastin’s primary function is to allow tissues to stretch and return to their original size. Your arteries, for instance, transport blood to and from your heart and to the rest of your body. Elastin makes the arteries stretchy enough to carry blood to the heart.You can find elastin in connective tissues, skin, blood vessels, and anywhere else in the body that needs to be able to stretch and recoil.
For instance, you can locate elastin in:
* Large arteries
* Heart valves
* Pulmonary tissues
* Ligaments
* Cartilage
* The liver
Where Can You Find Elastin?
Elastin can be found in the skin’s dermis layer. The elastin in your skin enables it to stretch and rebound: for instance, when you smile or eat.
Aging is a natural process, and you can’t avoid it. Unfortunately, as you age, the collagen and elastin in your body deteriorate, leaving your skin less firm and youthful.
As the result of elastin damage, you may observe:
* Thin skin
* Permanent frown or smile lines
* Wrinkles
* Loose, saggy skin
* Fine lines
What Conditions Affect Elastin?
The environment can play a significant role in the degradation of elastin. UV rays from the sun, for example, can damage elastin.
How Can You Keep Elastin Healthy?
When you get older, your elastin will decrease, and your skin will wrinkle. However, there are ways that you can slow down elastin depletion.
Some of these methods include:
* Using sunscreen
* Taking antioxidants
* Eating leafy greens, fruits, fish, and berries
* Drinking plenty of water
* Using moisturizers that contain Vitamin A, Vitamin E, and Vitamin C
* Exercising
* Not smoking
* Limiting excessive alcohol consumption
Collagen
You’ve probably come across the terms collagen and elastin in your research to improving appearance of skin. However, there are similarities and differences between elastin vs collagen, though. Collagen and elastin are the main fibres that form the extracellular matrix. Both are formed by cells called fibroblasts. Additionally, while both are proteins that work together in your connective tissue, collagen is responsible for skin strength and resilience and elastin provides flexibility to the skin and enabling it to return to its original shape or form. Collagen and elastin reside in your skin’s middle layer, called the dermis. This is the thickest of the three layers, accounting for about 90% of your skin’s thickness. There’s a lot going on in this layer, as it’s home to hair, oil, sweat glands, nerves, and blood vessels. Collagen fibers make up 90% of the skin, and elastin makes up 10%.Production and density of both decreases as a function of age, and results in sagging and wrinkling.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is a structural protein, the most abundant source protein in your body, and makes up the structure or framework of your cells and tissues. It’s the main component of connective tissues such as tendons, cartilage, ligaments, skin, and muscles. It’s important for healthy joints, bones, muscles, blood, and skin. It also makes up three-quarters of your skin and one-third of the protein in your body. Your body makes it naturally by combining amino acids, the building blocks of proteins found in food. To produce collagen, your body needs:
* Proline: Found in egg whites, dairy, cabbage, mushrooms, and asparagus
* Glycine: Found in pork skin, chicken skin, and gelatin and a variety of other protein-rich foods
* Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits and bell peppers
* Zinc: Found in beef, lamb, pork, shellfish, chickpeas, lentils, beans, milk, cheese, and various nuts and seeds
* Copper: Found in organ meats, cocoa powder, cashews, sesame seeds, and lentils
Different types of foods can help your body produce collagen. This process happens when your body combines amino acids like proline, glycine, vitamin C, zinc, and copper. As you age, your existing collagen breaks down, and it gets harder for your body to make more.
What Does Collagen Do?
Collagen provides your body with strength, structure, and support.L. As people grow older, their collagen becomes fragmented, fibroblast function becomes impaired, and collagen production slows. This is particularly true for females after you’ve gone through menopause. It’s because over time, your body increasingly struggles to absorb enough of the nutrients it needs to make collagen. However, eating collagen-rich foods can help your body overcome some of this absorption problem. That helps keep your body stronger and healthier as you get older.
Collagen also:
* Helps your blood clot
* Helps replace dead skin cells
* Creates a protective cover for your organs
* Allows new skin cells to grow
Types of Collagen
Your body contains many types of collagen. Scientists have identified a total of 29 varieties, including these five main types:
* Type I, which gives strength to your skin, bones, ligaments, and tendons
* Type II, which makes up the flexible cartilage that helps support your joints
* Type III, found in your internal organs, blood vessels, and muscles
* Type IV, in some layers of your skin
* Type V, which is present in your corneas and some layers of skin and
Collagen Supplements
Most collagen supplements contain types I, II, and III, which account for most of the collagen found in your body. They contain a digestible form of collagen called collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen. Most are hydrolyzed, which means the collagen has been broken down to make it easier to absorb.
These supplements are made from the tissues of cows, pigs, chickens, or fish. You can also buy vegan collagen powder made of bacteria and yeast. But scientists don’t know whether they have the same possible benefits as collagen from animal sources.
Collagen Peptides
Because collagen can’t be absorbed in its whole form, it has to be broken down into smaller amino acids or peptides. Collagen peptides are tiny pieces of animal collagen. It’s what’s in the collagen supplements you take and can come in many forms, including pills or powders. When you buy collagen, it’ll be sold as collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen. Collagen peptides are soaked up through your gastrointestinal tract.
Collagen Powder
Collagen powder has the same active ingredients as collagen capsules and gummies. But the dosages will vary depending on what form you use. Some people find it easier to add collagen powder to drinks or foods than to swallow several capsules. And you may not want the added sugar that’s in collagen gummies.
Collagen Liquid
You can also buy premade collagen drinks or packets of collagen to put in your choice of beverage. There are a variety of flavors and types to choose from. Many also have other beneficial ingredients.
If you take collagen supplements, they can count toward your daily protein needs—up to a point. Collagen has eight of the nine so-called essential amino acids your body needs in order to make protein.
The good news is that the missing amino acid, tryptophan, is found in lots of foods, including dairy, meats, seafood, tofu, nuts, and grains. Research shows that most people can get a third of their daily protein from collagen and still get all their essential amino acids.
Here are some commonly cited benefits of collagen supplements:
Stronger bones. As you age, your bones become less dense and more brittle, breaking more easily and taking longer to heal. Some research has found that taking daily collagen powder could help make your bones denser, slowing the aging process that makes them brittle and helping your body produce new bone.
Skin elasticity and hydration. Collagen supplements have been shown to improve skin hydration and elasticity in older people. They might also help lessen wrinkles. Several studies have shown that collagen peptides or supplements containing collagen may help slow the aging of your skin by reducing wrinkles and dryness. One review of 26 studies focusing mostly on women found that taking 1–12 grams of collagen per day for 4–12 weeks led to improvements in skin elasticity and hydration. These supplements may work
by stimulating your body to produce collagen and other proteins that help structure your skin, including elastin and fibrillin.
Thicker hair. While more men go bald, many women also have hair loss or thinning as they age. In one study, a group of women with thinning hair saw significant increases in their hair’s quantity, scalp coverage, and thickness while taking daily collagen supplements.
Healthier nails. Some people’s nails break more easily than others and don’t grow as fast. One study in a group of women showed faster nail growth and fewer broken or chipped nails after only 4 weeks of daily collagen supplements.
Reduced osteoarthritis pain. For people with knee osteoarthritis, collagen supplements might act as a mild pain reliever and improve joint function. It may take about 3-5 months of daily treatment before you see these improvements.
Increased muscle mass. One small study found that men who took collagen peptide supplements during a 12-week strength training program saw more increases in muscle mass and strength than those who didn’t.
Improved heart health. Collagen helps keep the shape of your arteries and blood vessels. When you lack collagen, your arteries may weaken. Fragile blood vessels increase the risk of atherosclerosis, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. A small study done on healthy people found that collagen powder kept arteries healthier and helped reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
Foods With Collagen
The effects of collagen powder and other supplements continue to be researched and debated.
To produce collagen, your body puts the amino acids glycine and proline together with other amino acids including vitamin C, zinc, and copper. You can help your body make more collagen by eating lots of glycine- and proline-rich foods. For vitamin C, zinc, and copper, you should also be sure to eat foods like papaya, citrus fruits, tomatoes, leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, shellfish, nuts, and whole grains.
Foods to add to your diet for more collagen include:
Bone broth. This is made by simmering animal bones and connective tissue for an extended period. The process extracts collagen from the bones and skin and puts it into the broth. Common animals used to make bone brothinclude chickens, cows, turkeys, and deer (venison).
Fish with the skin on. Fish is an excellent source of collagen from food, as long as you leave the skin on. That’s because much of the collagen found in fish is stored in the skin. Other benefits of fish include omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D.
Chicken. If you’ve ever prepared a whole chicken, you know there’s quite a bit of connective tissue in the meat. This makes chicken a good option for adding more collagen to your diet. Chicken feet in particular, while not a common food in some parts of the world, are a good source of collagen.
Red meat. Tougher cuts of meat like pot roast, chuck steak, and brisket, which are full of connective tissue, are good sources of collagen. But keep in mind that red meat gives you other nutrients you may not want, like saturated fat. Fruits and vegetables. For vegetarians and vegans, consider eating foods high in vitamin C. Eating foods rich in this nutrient encourages your body to make its own collagen and keep you healthy and strong.
Aloe vera. Low doses of aloe vera can boost the collagen in your dermis (which is the middle layer of skin). A study found that taking a 40-microgram aloe supplement a day can help with skin barrier function, elasticity, and moisture.
Other high-protein foods. Foods high in protein help collagen production because they have a lot of amino acids. These include eggs, dairy, and beans.
How to Prevent Collagen Loss
While collagen loss and damage as you age are inevitable, certain dietary and lifestyle factors can accelerate this process.
For example, smoking cigarettes is known to degrade collagen and cause skin aging, wrinkles, and loss of elasticity.
Excessive drinking has also been shown to accelerate skin aging by reducing collagen production and damaging skin repair mechanisms.
Additionally, following a diet high in added sugar and ultra-processed foods can lead to premature aging by contributing to a process called glycation, which reduces collagen turnover and interferes with collagen’s ability to interact with surrounding cells and proteins. Avoiding or reducing your intake of certain foods and beverages while increasing your consumption of others may help support collagen maintenance and overall skin health. For example, a diet low in compounds called advanced glycation end products (AGEs) may help promote skin health. AGEs are toxins that accumulate in the skin. They can cause collagen to stiffen and can inactivate proteins responsible for collagen repair. Foods highest in AGEs include processed meat products like hot dogs and bacon, fried foods like french fries and fried chicken, and roasted and grilled meats, according to newer and older research. Additionally, following a diet high in high quality protein and plant foods such as fruits and vegetables, which contain collagen-supportive and protective nutrients, may also help protect collagen stores and prevent collagen damage and loss.
Excessive sun exposure degrades collagen production as well, so wearing sunscreen and avoiding excessive sun exposure can help prevent signs of premature skin aging.
Takeaways
Collagen helps with healthy joints, skin elasticity, and more. Your body makes it naturally, and you can consume it. It’s in certain foods, but you can also get it from drinks or supplements. Just make sure you get your supplements from a trustworthy and high-quality brand.
Aesthetic Treatments and Skincare to Promote Collagen and Elastin
Although this post has more technical terms, it’s based on a scholarly article that has useful information explaining collagen and elastin.
Antioxidants (Vitamins A, C and E, trace elements such as selenium, copper and zinc, polyphenols, flavonoids, glutathione, peroxidases and superoxide desmutases) prevent degradation of tissues caused by free radicals.
Retinoids are compounds that are chemically related to Vitamin A and there are various forms. Biochemical changes brought about by retinoids in non-medical terms, simply results in marked increase in epidermal cell layer thickness and prevents collagen degradation.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) aids in the structure of collagen and is needed in the cross-linking process to promote elasticity
Additionally, it is necessary for collagen synthesis, so having low or deficient levels of vitamin C can lead to impaired collagen production. Vitamin C induces a dose-dependent increase in collagen Type I deposits by normal human fibroblasts. In a study by Fitzpatrick and Rostan a formulation of Vitamin C – 10% ascorbic acid (water soluble) and 7% tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate (lipid soluble) resulted in clinically visible and statistically significant improvement in wrinkling when used topically for 12 weeks.
Hydrolysed collagen made from native peptides found in animals consists of small peptides with low molecular weight, enriched in specific amino acids. Due to its low molecular weight, hydrolysed collagen is highly digestible, absorbed and distributed in the different tissues of the human body. In the dermis, hydrolysed collagen has a dual action mechanism – (a) free amino acids provide building blocks for the formation of collagen and elastin fibres, (b) collagen oligopetides act as ligands, binding to receptors present on the fibroblasts’ membrane and stimulate the production of new collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid (HA). A review of 19 studies that included 1,125 participants (95% women) between the ages of 20 and 70 found that taking hydrolyzed collagen improved skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles compared with placebo treatments.
Various energy based technologies like radio-frequency (RF), infra-red and deep ultrasound are available that trigger neocollagenesis and help to firm, tighten, lift and smoothen skin.
Neocollagenesis – occurs in the human body as a natural component of wound repair. The formation of new collagen in scars results from an inflammatory response to injury. This inflammation produces increased fibroblast stimulation and collagen deposits.
Another option to stimulate more collagen would be microneedling, or collagen-induction therapy. By microneedling, your esthetician creates controlled damage to the skin, and actually produces microscopic punctures in the skin. Your skin, by nature, actually produces more collagen to repair itself, and the collagen will then create a “scaffolding” affect and will fill in the separated area/ puncture. Cell Reactivate is another treatment series that will assist the skin in creating more collagen. While collagen is fairly easy to stimulate (by a professional), elastin is much harder to stimulate and produce. Microcurrent, however, is one of the only treatments that has actually been proven to stimulate to the reproduction of elastin.
In a study from 2006 by Dr. Laaff, a dermatopathologist, he evaluated twenty blinded biopsies from a study performed by Dr. M. Schwarz, a plastic surgeon, into the effects of the derma roller device on collagen and elastin formation. Biopsies were taken from various parts of the body of ten patients undergoing elective cosmetic surgery. A first ‘control’ biopsy was taken adjacent to the site that was needled with the derma roller. Six to eight weeks later, another biopsy was taken from the needled skin. New collagen and elastin fibre formation was obvious and quite dramatic. On average, an increase of new fibres of 206% was observed.
Ref: webMD and healthline